On-chain storage was pioneered by Larva Labs in their Autoglyphs generative art NFT project, the same Larva Labs that created CryptoPunks and V1 CryptoPunks.
What Is Meant By “On-Chain” In NFTs?
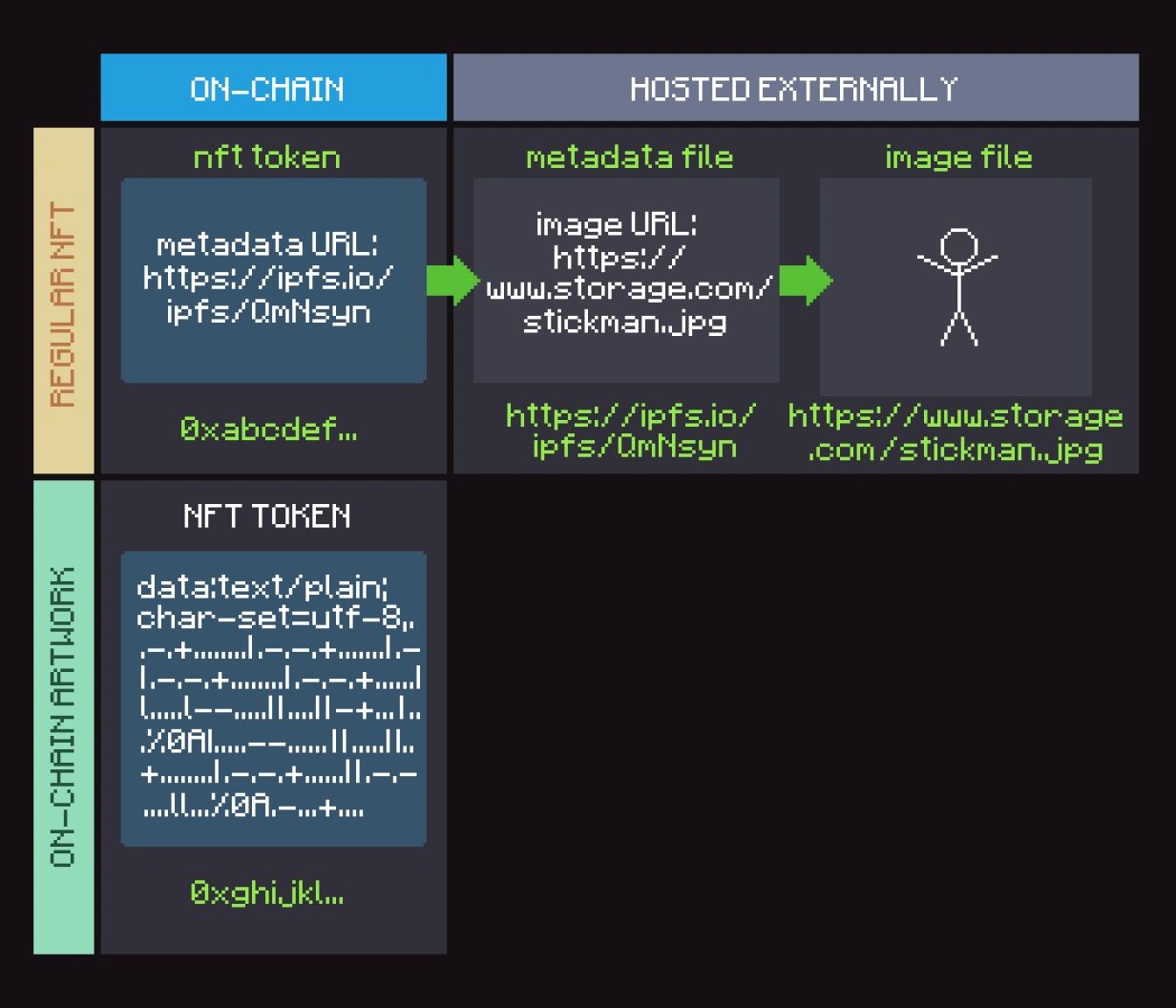
“On-chain” refers to where the core components of an NFT exist, where they are stored. Whereas in an off-chain NFT collection metadata and media are hosted externally, in an on-chain NFT collection an NFT’s token, metadata, and media are all hosted on a blockchain. The NFT artwork, for example, is stored within the token itself, making the image attached to that token as immutable as the blockchain itself.
Types of data and media typically stored on-chain include, but are not limited to, names, descriptions, date created, trait and trait rarities, license information, images, videos, and complete transaction histories – essentially, all the information one would need in order to prove origin and ownership.
Not On-Chain, Not Your NFT
In the case of the NFT utilizing an off-chain storage method, the only on-chain component is the token itself. This means that the metadata and media of the NFT can be changed, deleted, or even taken from the NFT owner. However, in the case of on-chain storage, the NFT truly becomes permanent artwork – the token itself hosts all metadata and media, securing the longevity and value of the asset.
The image below illustrates these essential differences between on-chain and off-chain storage.
What Are The Benefits Of On-Chain Storage?
Establishing provenance, permanence, ownership, and control by storing an NFT asset’s complete metadata and transactional history directly on a blockchain, benefits of on-chain storage for NFT collectors and collection include:
- Auditability
- Control – No Intermediaries or Third Parties
- Decentralization
- Durability
- History
- Immutability
- Increased Liquidity
- Increased Value
- Ownership
- Permanence
- Provability
- Provenance
- Reliability
- Security
- Transparency
- Territorial Sovereignty
Final Thoughts
While it is true that complete, corroborated, transparent, and provable ownership are clearly defined in the case of on-chain NFTs, this is not always true for an on-chain NFTs origin story or history. Furthermore, in the case where an NFT is a derivation, there is often no on-chain record pointing from the work upon which the NFT is derived. There can be no question that on-chain NFTs well-serve in establishing provenance, but one cannot fairly argue that this provenance is always perfect.